Catatonic schizophrenia - severe mental disorder, in which psychomotor disorders come to the fore: agitation and stupor, alternating alternately.
This form of schizophrenia is extremely rare: only 1-3% of all schizophrenic patients have it.
General information

Catatonic disorders are found not only in catatonic schizophrenia, but also in other diseases, including depression, organic brain damage, bipolar affective disorder, severe traumatic brain injury, and neoplasms in the brain tissues.
Therefore, it is important that a complex of examinations in cases of suspected catatonic schizophrenia be controlled by qualified specialists.
Psychomotor Disorders manifest in other forms of schizophrenia, especially in hebephrenia, but are not prevalent.
In addition to psychomotor disorders, there are other symptoms: negativism, mutism.
This form of schizophrenia is considered one of the most severe, and in most cases the prognosis for it is unfavorable or conditionally unfavorable.
However, the treatment started on time and the right set of drugs can improve the patient's condition.
Most often catatonic schizophrenia develops in 16-25 years. In boys, the first signs of the disease appear earlier than in girls.
Causes of development
The main causes of catatonic schizophrenia:
 Genetics. The likelihood of developing schizophrenia is many times greater if among the close relatives of a person were people with this disease or other severe mental disabilities. This is due to the fact that the child could get a defective gene, which over time will lead to the development of disorders in brain activity. But at least half of the cases of schizophrenia are associated with random mutations of the gene at the time of conception.
Genetics. The likelihood of developing schizophrenia is many times greater if among the close relatives of a person were people with this disease or other severe mental disabilities. This is due to the fact that the child could get a defective gene, which over time will lead to the development of disorders in brain activity. But at least half of the cases of schizophrenia are associated with random mutations of the gene at the time of conception.- Adverse pregnancy, birth trauma, hypoxia. The risk of developing catatonic schizophrenia increases if the mother during the period of pregnancy suffered infectious diseases (chickenpox, measles, rubella, hepatitis, influenza and others), used drugs, smoked, drank alcohol. Also, some chronic diseases of the mother can adversely affect the process of formation of the brain of the fetus (for example, heart failure).
- Psycho-emotional turmoil. These include single or multiple episodes of violence (psychological, sexual, physical), prolonged severe stress, the death of dear people, military actions, separation from the mother, quarrels in the family, the divorce of parents and much more.
- Problems in the social aspects of life. Schizophrenia is more common in people with a vagabond lifestyle. Lack of nutrition, especially when carrying a child and in the first years of his life, also has an adverse effect on the formation of the brain. In addition, forced migration, alcoholism and drug addiction of parents influence the development of schizophrenia.
 Addiction to drugs and alcohol. Most often, the occurrence of schizophrenia results from taking drugs of the hallucinogenic type (LSD, mescaline, psilocybin), since they most strongly affect the psyche and significantly change the perception of reality.
Addiction to drugs and alcohol. Most often, the occurrence of schizophrenia results from taking drugs of the hallucinogenic type (LSD, mescaline, psilocybin), since they most strongly affect the psyche and significantly change the perception of reality.- Personality features. Schizophrenia is most susceptible to people with a pronounced burden of perfectionism: the so-called “excellent student syndrome”, in which the desire to do everything as best as possible is prevailing, due to which a person is in constant tension.
The process of the flow of labor also matters: head injuries, prematurity, oxygen starvation - all this can affect the development of mental abnormalities.
In premature babies, the risk of developing schizophrenia is doubled.
Symptoms and signs
The basis of catatonic schizophrenia are two pathological conditions:
- stupor The patient freezes in one position (usually he lies or sits), his condition is inhibited, he defecates in the same place where he is, without changing his position. It is useless to contact him: he does not speak, he practically does not react to external speech. If you do nothing, they form bedsores. The stupor lasts on average from several hours to several days;
- excitation. Appears before stupor or after it. The patient becomes hyperactive, dangerous for himself and others. He performs various actions, may be cruel, cause harm to people, destroy objects, so it is important that there is nothing next to him during these periods that could harm him: there should be no beating, sharp objects in the room.
About how catatonic stupor manifests itself, you can learn from this video:
The main symptoms of the disease:
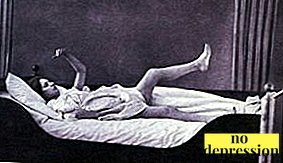 Wax flexibility. Can be observed with a stupor. In this condition, the patient retains for a long time the position that a stranger gave him (see photo). Airbag syndrome is often observed: if the patient’s head is raised above the pillow, it will freeze in this position, and free space will remain between his head and the pillow.
Wax flexibility. Can be observed with a stupor. In this condition, the patient retains for a long time the position that a stranger gave him (see photo). Airbag syndrome is often observed: if the patient’s head is raised above the pillow, it will freeze in this position, and free space will remain between his head and the pillow.- Negativism. It is divided into active, paradoxical and passive. With an active patient, he refuses to perform the actions that he was asked to perform, does anything, except for what is needed, while paradoxically he performs the exact opposite of what he was asked.
- Oneiroid syndrome. Observed during catatonic stupor. The patient sees in front of him pictures of different content, but most often fantastic. They can be both depressive, anxious, and majestic, manic. The patient is present in the oneiric as a participant or as an observer. Oneiroid syndrome is not always observed in catatonic schizophrenia.
- Catatonic mutism. The patient does not respond to attempts to address him, is silent and does not show his willingness to engage in dialogue, despite the fact that his own speech is saved and he can comprehend what he heard. In some cases, there is no reaction only to phrases spoken loudly, but if you speak with him in a whisper, he will respond. This is called Pavlov syndrome.
 Stereotypes The patient can continuously repeat various words, actions, phrases, but in this repetition there is no meaningfulness. Stereotypes can be different, from simple (the patient is swinging, nodding his head) to complex (marching).
Stereotypes The patient can continuously repeat various words, actions, phrases, but in this repetition there is no meaningfulness. Stereotypes can be different, from simple (the patient is swinging, nodding his head) to complex (marching).- Symptom proboscis. The patient pulls the lips into a tube. It may take several minutes or several hours.
- The symptom of the hood. It is expressed in the desire of the patient to pull something over the head (the edge of the robe, the hood) and take the position of the embryo.
- Passive obedience. The patient stays idle until he receives instructions about what he needs to do.
Passive negativism is ignoring requests, instructions, and in principle any appeals. If you try to feed or clothe him, he will resist.
If the patient does not have the neuroid syndrome, this is an unfavorable prognostic sign.
Symptoms of the disease are shown in this video:
Diagnostics
In the process of diagnosis, the doctor monitors the presence of symptoms characteristic of catatonic schizophrenia, and, if there is at least one of them, diagnoses. Observation must last at least two weeks.
Also held differential diagnosis which allows to distinguish catatonic schizophrenia from other pathological conditions, such as:
- encephalitis;
- neoplasms in brain tissue;
- temporal lobe epilepsy;
 mania;
mania;- depression;
- hepatocerebral dystrophy;
- sodium deficiency;
- swelling of the brain;
- Tay-Sachs disease;
- effects of taking certain drugs (ecstasy, cocaine, ciprolet).
The patient is directed to an electroencephalogram, magnetic resonance and computed tomography to make sure there are no tumors, epileptoid activity. If necessary, the attending physician will refer you to additional examinations that will clarify the diagnosis.
Treatment
Sick being treated in hospital. There, it is easier to control the condition of patients than at home, and the likelihood that a person will receive any injuries during arousal or injure someone is minimized.
When patients are in a state of stupor, they are also looked after; if necessary, droppers with nutrients are placed.
Catatonic schizophrenia is treated with the use of specially selected medication, which include:
 Antipsychotics. They are used to calm the patient when he is in a state of catatonic arousal. Used drugs belonging to the class of benzodiazepines, which eliminate anxiety, have hypnotic and anticonvulsant effect. Classic antipsychotics are used if the patient is aggressive, behaves asocially. In catatonic schizophrenia, the main antipsychotics are used with caution. Examples of drugs: Triazolam, clonazepam, lorazepam, haloperidol, diazepam.
Antipsychotics. They are used to calm the patient when he is in a state of catatonic arousal. Used drugs belonging to the class of benzodiazepines, which eliminate anxiety, have hypnotic and anticonvulsant effect. Classic antipsychotics are used if the patient is aggressive, behaves asocially. In catatonic schizophrenia, the main antipsychotics are used with caution. Examples of drugs: Triazolam, clonazepam, lorazepam, haloperidol, diazepam.- Nootropic drugs. Introduced to the patient who is in a state of catatonic stupor. Activate brain activity, improve blood flow. Examples: Piracetam, Cinnarizine.
- Normotimy means. Aimed at normalizing mood. Examples: Carbamazepine, lithium preparations, olanzapine.
- Muscle relaxants. Reduce arousal in skeletal muscle. Examples: Tercuronium, Tubocurarin.
If the drug treatment was not sufficiently effective, it is possible to electroconvulsive therapyin which discharges of electric current are passed through the patient's body. However, this method is very controversial and causes a large amount of discomfort to patients.
For example, Ernest Hemingway, a famous American writer, committed suicide due to the fact that his cognitive functions were significantly weakened after treatment.
Forecast

With catatonic form of schizophrenia, the prognosis is predominantly adverse: most patients gradually deteriorate their mental state, they are not able to take care of themselves.
It is also not always possible to bring a patient into stable remission in this form of schizophrenia, but medications allow reduce the incidence of catatonic symptoms and greatly facilitate the life of the sick.
They should keep track of their own condition throughout their lives. Many of them need help and care.
The sooner treatment of catatonic schizophrenia begins, the better the forecasttherefore, for people whose relatives have symptoms characteristic of this disease, it is important to do everything possible so that they receive medical assistance in time.

 Genetics. The likelihood of developing schizophrenia is many times greater if among the close relatives of a person were people with this disease or other severe mental disabilities. This is due to the fact that the child could get a defective gene, which over time will lead to the development of disorders in brain activity. But at least half of the cases of schizophrenia are associated with random mutations of the gene at the time of conception.
Genetics. The likelihood of developing schizophrenia is many times greater if among the close relatives of a person were people with this disease or other severe mental disabilities. This is due to the fact that the child could get a defective gene, which over time will lead to the development of disorders in brain activity. But at least half of the cases of schizophrenia are associated with random mutations of the gene at the time of conception. Addiction to drugs and alcohol. Most often, the occurrence of schizophrenia results from taking drugs of the hallucinogenic type (LSD, mescaline, psilocybin), since they most strongly affect the psyche and significantly change the perception of reality.
Addiction to drugs and alcohol. Most often, the occurrence of schizophrenia results from taking drugs of the hallucinogenic type (LSD, mescaline, psilocybin), since they most strongly affect the psyche and significantly change the perception of reality. Wax flexibility. Can be observed with a stupor. In this condition, the patient retains for a long time the position that a stranger gave him (see photo). Airbag syndrome is often observed: if the patient’s head is raised above the pillow, it will freeze in this position, and free space will remain between his head and the pillow.
Wax flexibility. Can be observed with a stupor. In this condition, the patient retains for a long time the position that a stranger gave him (see photo). Airbag syndrome is often observed: if the patient’s head is raised above the pillow, it will freeze in this position, and free space will remain between his head and the pillow. Stereotypes The patient can continuously repeat various words, actions, phrases, but in this repetition there is no meaningfulness. Stereotypes can be different, from simple (the patient is swinging, nodding his head) to complex (marching).
Stereotypes The patient can continuously repeat various words, actions, phrases, but in this repetition there is no meaningfulness. Stereotypes can be different, from simple (the patient is swinging, nodding his head) to complex (marching). mania;
mania; Antipsychotics. They are used to calm the patient when he is in a state of catatonic arousal. Used drugs belonging to the class of benzodiazepines, which eliminate anxiety, have hypnotic and anticonvulsant effect. Classic antipsychotics are used if the patient is aggressive, behaves asocially. In catatonic schizophrenia, the main antipsychotics are used with caution. Examples of drugs: Triazolam, clonazepam, lorazepam, haloperidol, diazepam.
Antipsychotics. They are used to calm the patient when he is in a state of catatonic arousal. Used drugs belonging to the class of benzodiazepines, which eliminate anxiety, have hypnotic and anticonvulsant effect. Classic antipsychotics are used if the patient is aggressive, behaves asocially. In catatonic schizophrenia, the main antipsychotics are used with caution. Examples of drugs: Triazolam, clonazepam, lorazepam, haloperidol, diazepam.

